Optimize Your Gaming PC: The Importance of Case Airflow
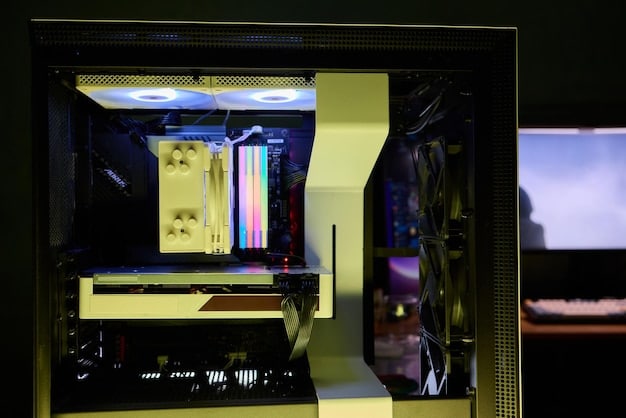

Optimizing case airflow is crucial for maintaining stable temperatures and maximizing the performance and longevity of your gaming PC components, preventing overheating and ensuring efficient heat dissipation.
Is your gaming PC underperforming or overheating? The secret might be in optimizing your case airflow. Proper airflow is essential for keeping your components cool and running at their best.
Understanding the Basics of Case Airflow
Case airflow is the movement of air through your computer case. Its primary purpose is to dissipate heat generated by components like the CPU, GPU, and motherboard. Without adequate airflow, heat builds up, leading to reduced performance and potential hardware damage.
Think of your PC case like a miniature ecosystem. Cool air enters the case, flows over the hot components, absorbs heat, and then exits the case. This constant flow of air is what keeps your system stable and prevents thermal throttling.
Why is Effective Airflow Crucial?
Effective airflow is not just about keeping things cool; it’s about maintaining optimal operating conditions for all your components. Here are a few key reasons why it matters:
- Prevents Overheating: Overheating can cause your components to throttle, reducing performance and potentially leading to permanent damage.
- Extends Component Lifespan: Keeping components cool helps extend their lifespan, saving you money in the long run.
- Maintains Performance: Stable temperatures mean your CPU and GPU can run at their maximum clock speeds without thermal throttling.
- Reduces Noise: Effective airflow allows fans to run at lower speeds, reducing overall system noise.
Optimizing case airflow is a fundamental aspect of building and maintaining a high-performance gaming PC. By understanding the basics, you can create a cooling strategy that keeps your components running smoothly and efficiently.
Identifying Heat Sources in Your Gaming PC
Before optimizing your case airflow, it’s important to understand where the heat is coming from. Identifying the main heat sources within your gaming PC allows you to target your cooling efforts effectively.
Different components generate different amounts of heat. Knowing which parts are the biggest contributors will help you prioritize your cooling strategy and make informed decisions about fan placement and cooling solutions.
Major Heat-Generating Components
Several components in your gaming PC are responsible for producing significant amounts of heat. Here are the primary culprits:
- CPU (Central Processing Unit): The CPU is a major heat source, especially during demanding tasks like gaming and video editing.
- GPU (Graphics Processing Unit): The GPU is often the hottest component in a gaming PC, especially high-end models.
- VRMs (Voltage Regulator Modules): VRMs on the motherboard regulate power to the CPU and can generate significant heat, especially during overclocking.
- RAM (Random Access Memory): While RAM doesn’t generate as much heat as the CPU or GPU, it still contributes to the overall thermal load.
By understanding the specific heat output of each component, you can strategically position cooling solutions to address the areas that need it most. This targeted approach ensures that your system remains stable and performs optimally.
Principles of Positive vs. Negative Air Pressure
Air pressure within your PC case plays a crucial role in determining how effectively it stays cool and clean. Understanding the principles of positive and negative air pressure can help you optimize your airflow setup.
Air pressure refers to the balance between the amount of air entering and exiting your case. The ideal pressure balance can minimize dust buildup and improve overall cooling efficiency.
Positive Air Pressure
Positive air pressure occurs when there is more air entering the case than exiting. This setup has several advantages:
- Reduced Dust Buildup: Positive pressure forces air out of the case through small openings, preventing dust from being sucked in.
- Improved Cooling: More intake fans provide a constant supply of cool air to the components.
However, positive pressure can also have drawbacks. It may require more fans to achieve the desired airflow, and the excess air can sometimes create turbulence, reducing cooling efficiency in certain areas.
Negative Air Pressure
Negative air pressure occurs when there is more air exiting the case than entering. This setup also has its advantages:
- Enhanced Exhaust: Negative pressure efficiently removes hot air from the case, which can be beneficial in certain configurations.
- Lower Component Temperatures: Rapid exhaust can help keep components cooler by quickly removing heat.
Negative pressure, however, tends to draw air in through every crack and opening in the case, leading to increased dust buildup. It may also cause some components to run hotter if they aren’t receiving enough direct airflow.
The ideal air pressure depends on your specific setup and environmental conditions. Experimenting with different fan configurations will help you find the optimal balance for your gaming PC.
Choosing the Right Case Fans for Optimal Airflow
Selecting the right case fans is essential for achieving optimal airflow. Not all fans are created equal, and understanding the different types and specifications will help you make informed decisions.
Case fans come in various sizes, speeds, and designs, each with its own set of benefits and drawbacks. Choosing the right fans can significantly impact your system’s cooling performance and noise levels.
Types of Case Fans
There are several types of case fans available, each designed for specific purposes:
- Intake Fans: These fans are designed to bring cool air into the case. They typically have a high CFM (cubic feet per minute) rating to maximize airflow.
- Exhaust Fans: These fans remove hot air from the case. They may have a higher static pressure rating to effectively push air through obstructions like heatsinks and radiators.
- PWM Fans: PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) fans allow for variable speed control, allowing you to adjust the fan speed based on temperature for optimal performance and noise levels.
- RGB Fans: These fans come equipped with customizable RGB lighting, allowing you to add a personalized touch to your gaming PC.
Consider the fan’s CFM (Cubic Feet per Minute) and static pressure ratings. CFM indicates the amount of air a fan can move, while static pressure measures its ability to push air through obstructions.
When selecting case fans, consider the size of your case and the number of fan mounts available. Choose fans that are compatible with your case and provide adequate airflow for your components.
Strategic Fan Placement for Enhanced Cooling
Proper fan placement is key to maximizing airflow and cooling efficiency. By strategically positioning intake and exhaust fans, you can create a consistent flow of air that effectively dissipates heat.
The goal is to create a path for air to flow through the case, drawing in cool air from the front and bottom and exhausting hot air from the top and rear. This directed airflow ensures that all components receive adequate cooling.
Front intake fans pull cool air into the case, providing fresh air to the CPU, GPU, and other components. Rear exhaust fans remove hot air from the case, preventing it from recirculating.
Recommended Fan Placement Strategies
There are several strategies you can use to optimize fan placement:
- Front Intake, Rear Exhaust: This is a common and effective setup, with front fans pulling in cool air and rear fans exhausting hot air.
- Top Exhaust: Adding top exhaust fans can help remove rising hot air, further improving cooling performance.
- Bottom Intake: Bottom intake fans can provide additional cool air to the GPU and other lower components.
Experiment with different fan configurations to find the setup that works best for your specific case and components. Monitoring your system’s temperatures will help you determine the effectiveness of each configuration.
Maintaining Your Case Airflow for Long-Term Performance
Maintaining your case airflow is essential for ensuring long-term performance and reliability. Over time, dust and debris can accumulate, reducing airflow and increasing temperatures.
Regular maintenance can help prevent these issues, keeping your components cool and running smoothly. A clean system not only performs better but also lasts longer.
Regular Cleaning and Maintenance Tips
Here are some tips for maintaining your case airflow:
- Clean Dust Filters: Regularly clean the dust filters to prevent buildup, ensuring optimal airflow.
- Dust the Interior: Use compressed air to remove dust from the interior of the case, including fans, heatsinks, and other components.
- Check Fan Operation: Periodically check that all fans are functioning properly, replacing any that are failing or making excessive noise.
Implement these tips into your maintenance routine to keep system running smoothly for years to come.
| Key Point | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| 💨 Airflow Basics | Moving air through the case to dissipate heat and prevent component throttling. |
| 🔥 Heat Sources | CPU, GPU, VRMs, and RAM generate the most heat and require effective cooling. |
| ➕ Pressure Balance | Positive pressure reduces dust; negative enhances exhaust. Experiment to find the balance. |
| 🛠️ Fan Maintenance | Regular cleaning and maintenance prevent dust buildup, ensuring optimal airflow. |
Frequently Asked Questions
▼
Case airflow is critical because it dissipates heat generated by components like the CPU and GPU, preventing overheating and ensuring stable performance during gaming sessions. Good airflow extends the lifespan of your components.
▼
The best fan placement typically involves front intake fans to bring in cool air and rear/top exhaust fans to remove hot air. Experimenting with different configurations and monitoring temperatures will help dial it in.
▼
Positive air pressure means more air is entering the case than exiting, reducing dust buildup. Negative air pressure means more air is exiting the case, enhancing exhaust but potentially increasing dust. It’s a balancing act.
▼
You should clean the dust filters every 1-3 months, depending on the environment. More frequent cleaning is needed in dusty environments to maintain optimal airflow and prevent overheating.
▼
Yes, you can improve case airflow by optimizing cable management to reduce obstructions, cleaning dust from existing fans and components, and ensuring proper fan placement based on your case layout. Re-seat fans for the best results.
Conclusion
Optimizing your case airflow is a critical aspect of building and maintaining a high-performance gaming PC. By understanding the principles of airflow, selecting the right fans, and strategically placing them within your case, you can ensure that your components stay cool, perform optimally, and have a longer lifespan. Regular maintenance will keep your system running smoothly for years to come.





